Microsoft Interoperability API (Word)
A free API package for interoperability with Microsoft products is now available on neurons. The first version allows you to convert Microsoft Word documents (saved using Open XML SDK, i.e. .docx documents) to Markdown. This can be used for presentation purposes, or for the purposes of creating smart contracts, etc. It is an optional component that can be installed by the neuron operator. The API is protected, and requires either a login (using user accounts defined by the Admin-interface; no special privileges), or a JWT token issued by the neuron (available to clients connected via XMPP, for instance), or being logged in through a web session. The API cannot be accessed anonymously.
| Some more information | |
|---|---|
| Package | TAG.MicrosoftInterop.package |
| Installation key | Y/0hf+O003/pMh6CDnQTowb3DMJj3X28Xu0H0/bOPsIdGo+XOGY2kWsEyxkpKMSNdAOjSGDlxUIA00c066163c7125123382bdd308a2ad35 |
| More information | https://github.com/Trust-Anchor-Group/MicrosoftInterop |
Markdown Lab
Once the package has been properly installed, it will insert itself into the Markdown Lab on the Neuron®. It introduces an INPUT field that allows you to upload a Word document to the server, and convert it to Markdown, on the page. This way, you can experiment with the conversion capabilities provided. If you want to have documents for testing purposes, the repository contains a set of testing documents.

Internet Content Decoder and Converter
The package contains an Internet Content decoder for MS Word documents. This means you can build your own web services, and similar tools, that receive Word documents as content, and they will be automatically decoded. There’s also an Internet Content converted from Word to Markdown that can be used to publish Word documents directly on the site. These documents will be automatically converted to Markdown, and from Markdown to any other accepted format (like HTML), if the request indicates that the client only accepts HTML, for instance. This allows you to publish content directly using Word documents, without the need to converting them manually first.
Formatting Support
Microsoft Word supports a very rich set of features for formatting content in their documents. Markdown on the other hand, is not designed for creating formatted content in the same way, so a 1-to-1 conversion is not possible. But basic formatting constructs can be converted successfully. The following lists should give you an idea of what is supported and not.
Supported
- Sections
- Multiple columns
- Paragraphs and justifications (Left, Right, Center, Justify)
- Simple formats, such as Bold, Italic, Underline, Strike Tough, Superscript, Subscript, Insert, Delete, inline code
- Block code
- Horizontal separators
- Some fields and form input controls
- Tables, column spans
- Lists (Bullet-point lists, numbered lists, mixed lists)
- Table of contents
- Images & Figures
- Captions
- Frame contents
- Footnotes
- Endnotes
Not Supported (examples)
- Languages
- Positioning
- Colors
- Fonts
- Sizes
- Pages
- Headers
- Footers
- Macros
- Some fields and form input controls
- Row spans in tables
- Custom list formats.
- Indexes, Bibliographies, etc.
- Drawings and Shapes
- Frame position and layout.
Logging of unrecognized elements
If converting a Word document that contains elements the package library does not understand, information about these items will be logged to the event log. You can use this information to extend support to such items in the repository.
API Endpoint
API interface for the Word -> Markdown conversion is very simple. You execute a POST to the /MicrosoftInterop/WordToMarkdown resource on the Neuron® where the package is installed. The contents of the POST is the actual Word document. The response will be Markdown.
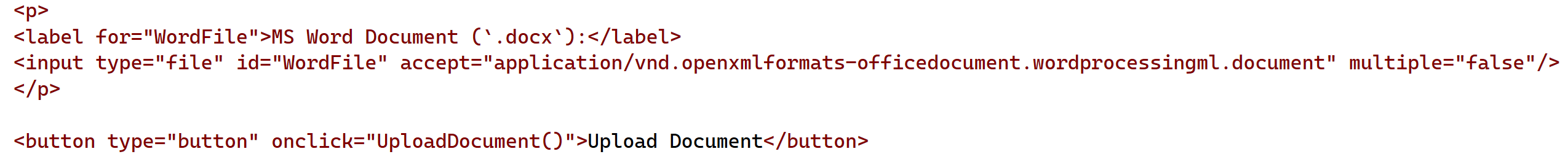
Example code
The following Markdown snipped, with associated Javascript function call, will call the API, and convert a Word document provided via a file INPUT tag, and place it into a TEXTAREA tag on the page. This code is inserted into the Markdown Lab available to logged in users with sufficient privileges on the Neuron®: